JavaScriptConcepts
JavaScript Closures: In-Depth Guide with Examples
A closure is a function that has access to the parent scope, even after the parent function has closed. A closure is formed when a function remembers the variables fro its lexical scope even when the function is executed outside its lexical scope.
1. Basic Closure Example
function outerFunction() {
let outerVariable = 'I am from outer!';
function innerFunction() {
console.log(outerVariable);
}
return innerFunction;
}
const closure1 = outerFunction();
closure1(); // Output: I am from outer!
Explanation:
innerFunctionforms a closure overouterVariablefromouterFunction.- Even after
outerFunctionfinishes,innerFunctioncan accessouterVariable.
2. Closure with Private Variables (Data Encapsulation)
function makeCounter() {
let count = 0;
return function() {
count++;
return count;
};
}
const counter = makeCounter();
counter(); // 1
counter(); // 2
counter(); // 3
Explanation:
countis private to the returned function, not accessible from outside.- Each call to
counter()increments and returns the privatecount.
3. Closures in Loops (Common Pitfall & Solution)
Problem:
var funcs = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
funcs.push(function() {
console.log('Problem:', i);
});
}
funcs[0](); // 3
funcs[1](); // 3
funcs[2](); // 3
Solution 1: IIFE
var funcsFixed = [];
for (var j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
(function(jCopy) {
funcsFixed.push(function() {
console.log('Fixed:', jCopy);
});
})(j);
}
funcsFixed[0](); // 0
funcsFixed[1](); // 1
funcsFixed[2](); // 2
Solution 2: Use let
let funcsLet = [];
for (let k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
funcsLet.push(function() {
console.log('Let:', k);
});
}
funcsLet[0](); // 0
funcsLet[1](); // 1
funcsLet[2](); // 2
Explanation:
- Using
varcauses all functions to share the same variable. - IIFE or
letcreates a new scope for each iteration.
4. Closures for Function Factories
function makeMultiplier(multiplier) {
return function(x) {
return x * multiplier;
};
}
const double = makeMultiplier(2);
const triple = makeMultiplier(3);
double(5); // 10
triple(5); // 15
Explanation:
makeMultiplierreturns a function that remembers themultipliervalue.
5. Closures in Asynchronous Code
Problem:
for (var m = 0; m < 3; m++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('Async Problem:', m);
}, 100);
}
// All log 3
Solution:
for (let n = 0; n < 3; n++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('Async Fixed:', n);
}, 200);
}
// Logs 0, 1, 2
Explanation:
letcreates a new binding for each iteration, so closures capture the correct value.
6. Practical Example: Hiding Implementation Details
function Person(name) {
let _name = name;
return {
getName: function() { return _name; },
setName: function(newName) { _name = newName; }
};
}
const p = Person('Alice');
p.getName(); // Alice
p.setName('Bob');
p.getName(); // Bob
Explanation:
_nameis private, only accessible viagetNameandsetName.- Demonstrates data privacy using closures.
7. Interview Question: What is a closure?
A closure is a function that remembers its lexical scope even when the function is executed outside that scope. It allows functions to access variables from an enclosing scope, even after that scope has closed.
8. Interview Question: Why are closures useful?
- Data privacy (private variables)
- Function factories
- Partial application/currying
- Event handlers and callbacks
- Maintaining state in async code
9. Advanced: Currying with Closures
function add(a) {
return function(b) {
return a + b;
};
}
const add5 = add(5);
add5(10); // 15
Explanation:
addreturns a function that remembersa.- This is the basis for currying and partial application.
10. Memory Leaks and Closures
Be careful: Closures can cause memory leaks if they retain references to large objects unnecessarily. Always clean up references if not needed.
Example:
function createLeak() {
let largeArray = new Array(1e6).fill('leak'); // Large object
return function() {
// This closure keeps largeArray in memory
console.log('Still holding largeArray of length:', largeArray.length);
};
}
let leaky = createLeak();
// Even if we don't need largeArray anymore, it's not garbage collected
// because the closure (leaky) still references it.
// To avoid the leak, set leaky = null when done:
// leaky = null;
Summary
Closures are a powerful feature in JavaScript, enabling data privacy, function factories, and more. Understanding closures is essential for interviews and real-world development.
setTimeout, Closures, and Loop Pitfalls
This section explains how closures interact with setTimeout and loops, a common source of confusion in JavaScript.
Example 1: The Problem with var in Loops
function y() {
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(i);
}, i * 1000);
}
}
y();
What happens?
- This will log
6five times (after 1s, 2s, …, 5s). - Why? Because
varis function-scoped, not block-scoped. By the time the callbacks run, the loop is done andiis6.
Example 2: Fix with IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression)
function z() {
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
(function(closeI) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(closeI);
}, closeI * 1000);
})(i);
}
}
z();
How does this work?
- The IIFE creates a new scope for each iteration, capturing the current value of
iascloseI. - Each timeout callback now has its own copy of the value.
- This logs
1, 2, 3, 4, 5as expected.
Example 3: Fix with let
function a() {
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(i);
}, i * 1000);
}
}
a();
How does this work?
letis block-scoped, so each iteration gets a new binding ofi.- Each callback closes over its own
ivalue. - This logs
0, 1, 2, 3, 4as expected.
Key Concepts
- Closures allow the callback to “remember” the variable from its surrounding scope.
- With
var, all callbacks share the same variable, leading to unexpected results in async code. - Use
letor an IIFE to capture the correct value for each iteration.
Summary:
When using asynchronous functions like
setTimeoutinside loops, always be mindful of variable scope. Useletor an IIFE to avoid common pitfalls with closures andvar.
Practice: Try modifying the examples in closures.js & setTimeOutPractice.js and observe the results to deepen your understanding.
scope in JavaScript
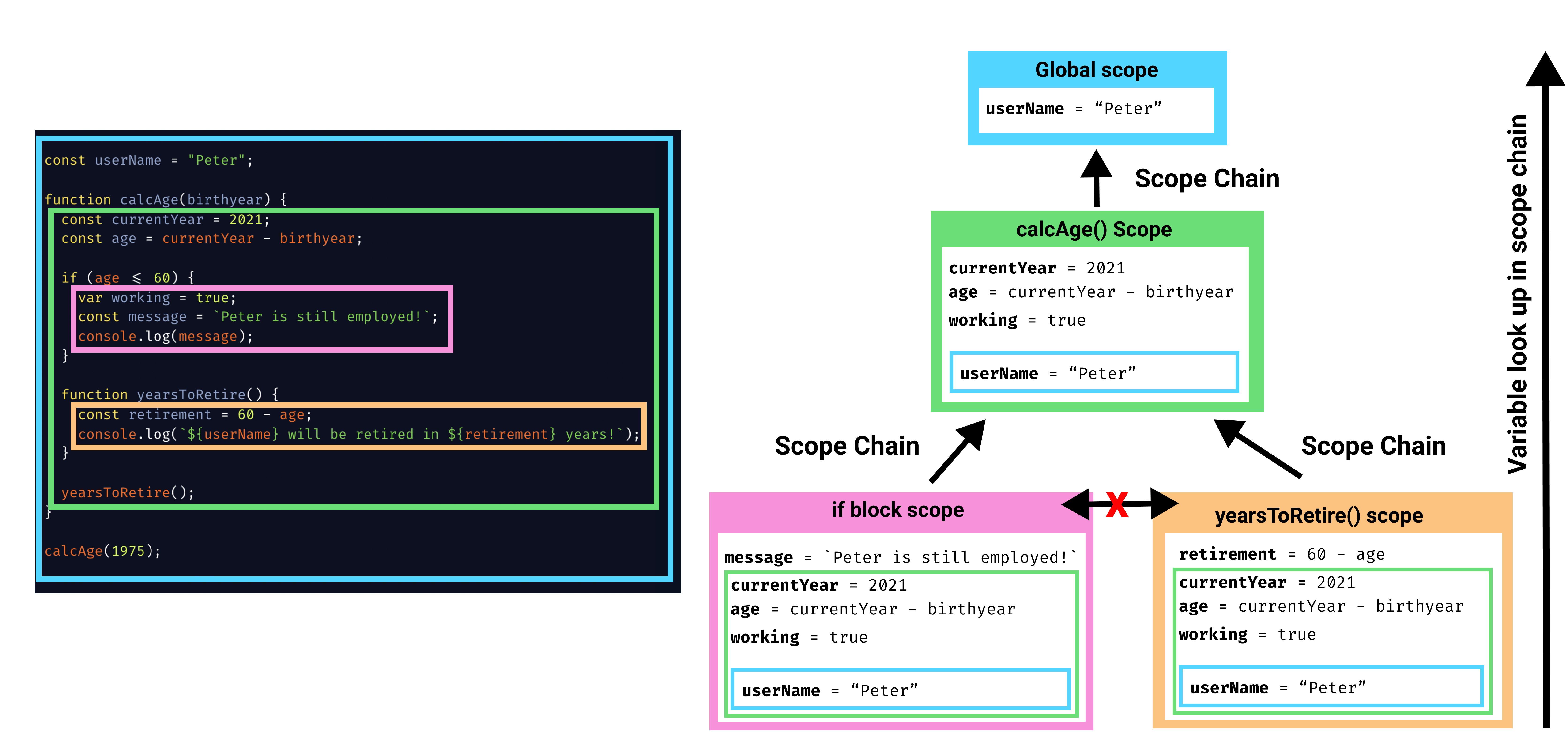

1. Scope — Formal Definition
Scope defines the region of the program where an identifier (variable, function, class) can be accessed.
JavaScript uses lexical (static) scoping, meaning:
- Scope is decided at code authoring time
- Not at runtime
- Based on physical nesting in source code
cope in JavaScript (Foundational Model)
Scope = where a variable is accessible in code. JavaScript scope is lexical (static), determined at parse time, not runtime.
1.1 Types of Scope
| Scope Type | Introduced By | Visibility |
|---|---|---|
| Global Scope | outside all functions | everywhere |
| Function Scope | function | entire function body |
| Block Scope | {} with let / const | block only |
| Module Scope | ES Modules | file-only |
let g = 10; // global
function f() {
let a = 1; // function scope
if (true) {
let b = 2; // block scope
}
}
Key rule:
var → function scoped
let / const → block scoped
2. Types of Scope in JavaScript
2.1 Global Scope
Declared outside all functions / blocks.
let a = 10;
function f() {
console.log(a);
}
- Lives for the entire lifetime of the program
- Pollutes namespace if overused
2.2 Function Scope
Created by function.
function test() {
var x = 5;
let y = 6;
}
xandyinaccessible outsidevaris function-scoped, not block-scoped
2.3 Block Scope
Created by {} only with let and const.
if (true) {
let a = 1;
const b = 2;
}
a,bexist only inside block- Prevents accidental overwrites
2.4 Module Scope (ES Modules)
// file.js
const secret = 42;
export {};
- Variables are private to file unless exported
- No implicit globals
3. Lexical Scope (Most Important Rule)
A function can access variables from its own scope and all parent scopes, determined by where it is written.
let x = 100;
function outer() {
let y = 200;
function inner() {
console.log(x, y);
}
inner();
}
innercan accessyandx- Parent cannot access child scope
Lexical scope is one-directional (inside → outside).
4. Scope Chain
When JavaScript resolves a variable:
- Look in current scope
- If not found, go to outer scope
- Continue until global scope
- If still not found →
ReferenceError
let a = 1;
function f() {
let b = 2;
function g() {
let c = 3;
console.log(a, b, c);
}
g();
}
Scope chain:
g → f → global
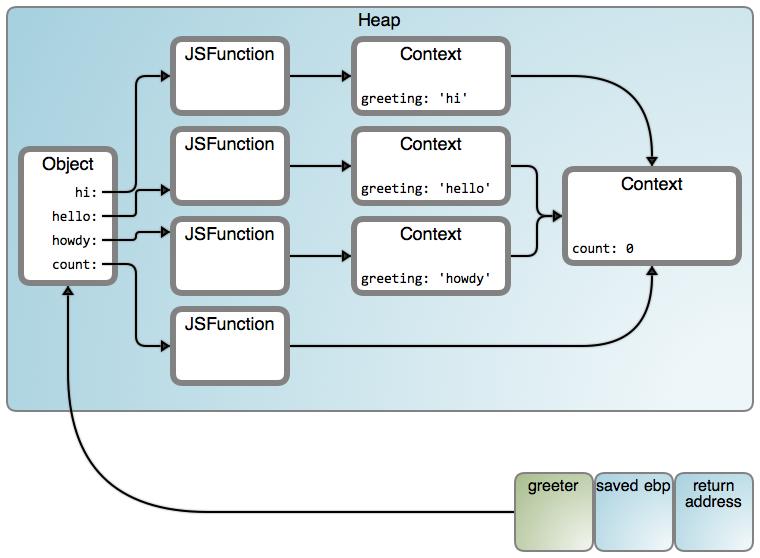
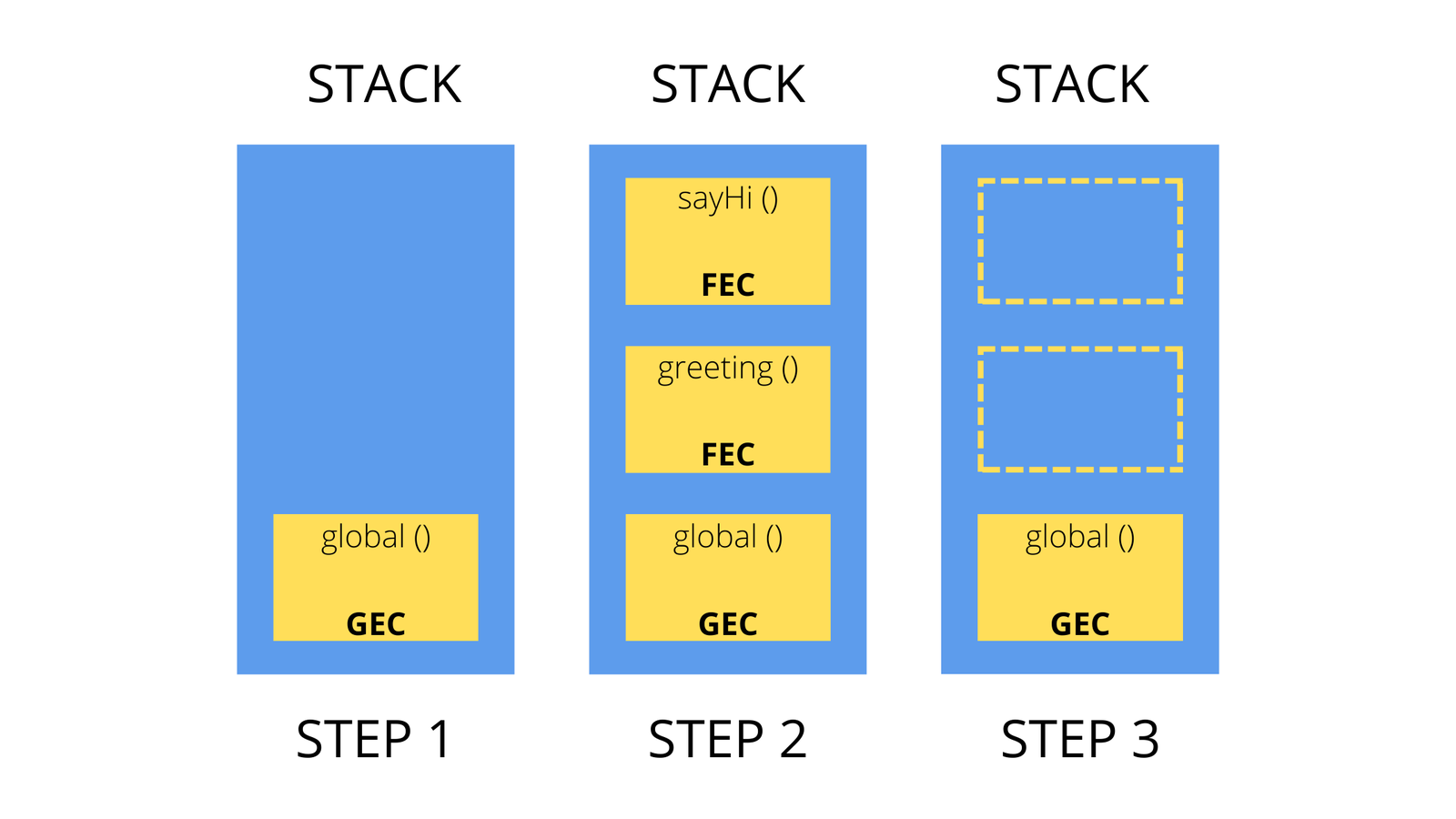
5. Execution Context Model (Internal Engine View)
Each function invocation creates an Execution Context containing:
- Variable Environment (
var, function declarations) - Lexical Environment (
let,const) - Outer Lexical Environment reference
Execution Contexts are pushed onto the Call Stack.
6. Closure — Formal Definition
A closure is a function that retains access to variables from its lexical environment even after the outer function has finished execution.
Closures are:
- Automatic
- Engine-level behavior
- Not created explicitly by syntax
7. Why Closures Exist (Key Insight)
Closures exist because:
- JavaScript uses lexical scoping
- Functions are first-class objects
- Returned functions keep references to outer variables
- Garbage collection preserves referenced variables
8. Closure Creation — Step-by-Step
function outer() {
let count = 0;
return function inner() {
count++;
return count;
};
}
const counter = outer();
Internal Behavior
outer()invokedcountcreated in lexical environmentinnerreturned- Call stack frame of
outerremoved countmoved to heapinnerholds reference tocount
counter(); // 1
counter(); // 2
9. Closure Retains Reference, Not Value
function test() {
let x = 10;
return () => console.log(x);
}
const fn = test();
x = 100; // unrelated
fn(); // 10
The closure references its own lexical environment, not global changes.
10. Multiple Closures, Independent State
function createCounter() {
let c = 0;
return () => ++c;
}
const c1 = createCounter();
const c2 = createCounter();
c1(); // 1
c1(); // 2
c2(); // 1
Each invocation creates a new lexical environment.
11. Common Closure Use Cases
11.1 Data Encapsulation (Private Variables)
function bankAccount(balance) {
return {
deposit(x) { balance += x; },
getBalance() { return balance; }
};
}
balancecannot be accessed directly- True privacy without classes
11.2 Function Factories
function multiplyBy(n) {
return x => x * n;
}
const double = multiplyBy(2);
const triple = multiplyBy(3);
11.3 Callbacks and Async
function fetchData() {
let token = "auth123";
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(token);
}, 1000);
}
Async does not break closure.
12. Classic Interview Bug — var in Loops
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(() => console.log(i), 0);
}
Output:
3
3
3
Explanation
varis function-scoped- Single shared
i - Closures capture same reference
Fix
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(() => console.log(i), 0);
}
13. Closure vs Scope (Critical Distinction)
| Aspect | Scope | Closure |
|---|---|---|
| What | Accessibility | Lifetime |
| Exists | Always | Only when referenced |
| Memory | Stack-based | Heap-retained |
| Purpose | Name resolution | State preservation |
14. Memory Implications (Advanced)
Closures can prevent garbage collection.
function heavy() {
let large = new Array(1e6);
return () => large.length;
}
As long as closure exists:
largeremains in memory
Mitigation:
large = null;
15. Closures in DSA / Real Systems
Closures are used in:
- Memoization
- Debouncing / Throttling
- Caching layers
- Iterators
- DFS recursion state
- React Hooks (
useStateis closure-based)
Memoization Example
function memoize(fn) {
const cache = {};
return function(n) {
if (cache[n]) return cache[n];
return cache[n] = fn(n);
};
}
16. Mental Model (One-Line)
Scope defines visibility. Closure defines persistence.
17. Interview-Grade Summary
- JavaScript uses lexical scoping
- Scope chain resolves identifiers upward
- Closures retain lexical environment via heap
let/constavoid shared reference bugs- Closures enable encapsulation and async state
- Misused closures cause memory leaks
encapsulation with closures
function bankAccount(balance) {
return {
deposit(x) { balance += x; },
getBalance() { return balance; }
};
}
balancecannot be accessed directly- True privacy without classes